Income Statement Items Explained With Examples
The income statement shows a company’s expense, income, gains, and losses, which can be put into a mathematical equation to arrive at the net profit or loss for that time period. This information helps you make timely decisions to make sure that your business is on a good financial footing. Revenues are the incomes that the company generates from the sale of goods or services or other activities related to the main operation of the company’s business.
The 4 Archetypes of the Private Equity CFO
Precise financial records require proper categorization of expenses and revenues. Errors often arise from misclassifications and omissions of one-time gains. Utilize accounting software and a detailed checklist to ensure accurate entries and comprehensive income tracking. At the bottom of the income statement, it’s clear the business realized a net income of $483.2 million during the reporting period. A balance report details your end balance for each account that will be listed on the income statement and provides all of the end balances required to create your income statement. You can also look at QuickBooks Online subscription levels and see a comparison of QuickBooks vs. Xero accounting software.
Calculate Gross Profit
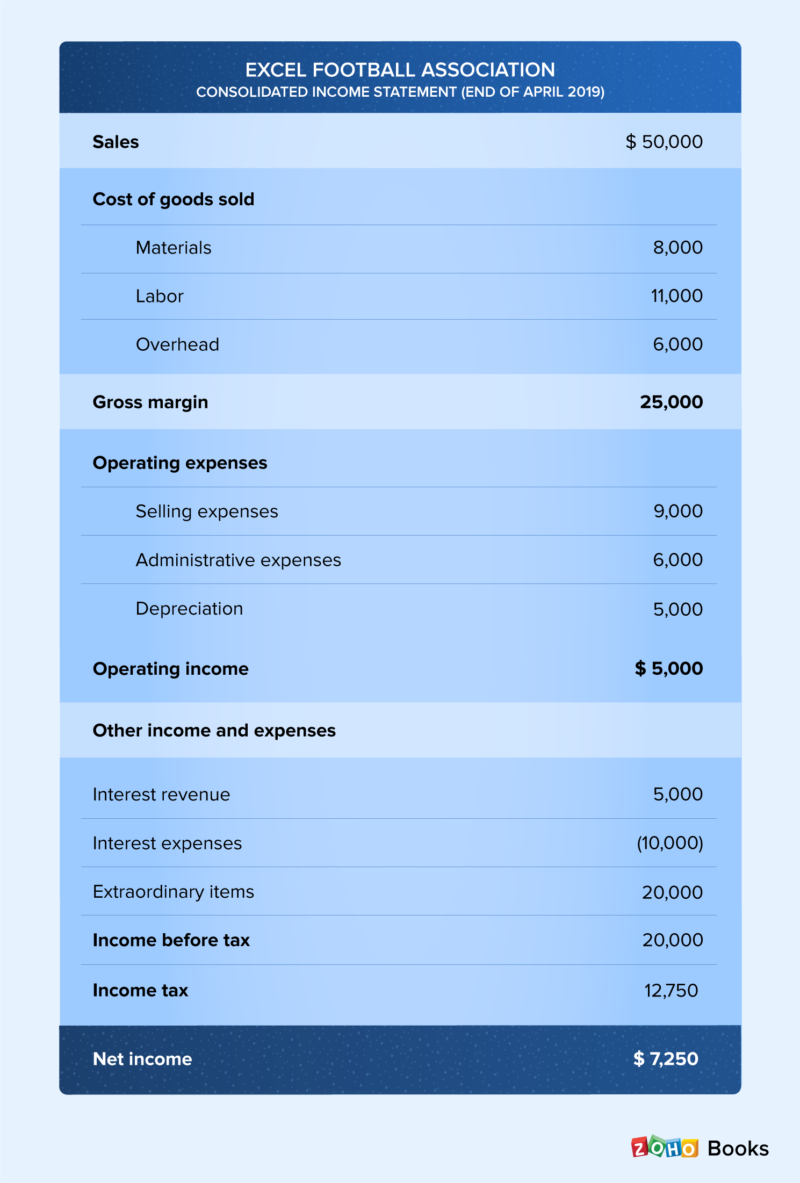
- It is calculated by subtracting SG&A expenses (excluding amortization and depreciation) from gross profit.
- Our platform features short, highly produced videos of HBS faculty and guest business experts, interactive graphs and exercises, cold calls to keep you engaged, and opportunities to contribute to a vibrant online community.
- Nonetheless, in 1978, the SEC required supplemental disclosures based on a variation of it for the oil and gas industry.
- In a qualitative sense, revenue can represent a reward obtained by providing goods or services to customers.
- Small businesses typically start producing income statements when a bank or investor wants to review the financial performance of their business to see how profitable they are.
- An income statement presents the revenues, expenses, and resulting profit or loss of a business.
The most common periodic division is monthly (for internal reporting), although certain companies may use a thirteen-period cycle. These periodic statements are aggregated into total values for quarterly and annual results. GAAP disclosure requirements are required to be disclosed in the tabular format only if the entire expense is included in a single relevant expense caption. Examples include disclosure of operating lease costs, warranty expense, gain on troubled debt restructuring, and foreign currency transaction gains or losses. Income statements or profit and loss accounts are financial statements used to calculate the financial health of the company. An income statement helps business owners decide whether they can generate profit by increasing revenues, by decreasing costs, or both.

Extraordinary Items
This number is arrived at by deducting the cost of revenue ($74 .1 billion) from the total revenue ($245.1 billion)—in other words, revenue minus the amount that it cost to make that $245.1 billion. Revenue realized through primary activities is often referred to as operating revenue. For a company manufacturing a product, or for a wholesaler, distributor, or retailer involved in the business of selling forms and instructions that product, the revenue from primary activities refers to revenue achieved from the sale of the product. In 2024, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) issued its highly anticipated climate change disclosure rules. Our publication provides some key disclosure and reporting reminders for upcoming filings and summarizes the SEC’s rulemaking and other activities that affect financial reporting.
Within an income statement, you’ll find all revenue and expense accounts for a set period. Accountants create income statements using trial balances from any two points in time. If you don’t have a background in finance or accounting, it might seem difficult to understand the complex concepts inherent in financial documents. However, taking the time to understand financial statements, such as learning how to read an income statement, can go far in helping you advance your career. In addition to helping you determine your company’s current financial health, understanding income statements can help you predict future opportunities, decide on business strategy, and create meaningful team goals. A multi-step statement splits the business activities into operating and non-operating categories.
Instead these expenses are reported on the income statement of the period in which they occur. An income statement is a financial report detailing a company’s income and expenses over a reporting period. It can also be referred to as a profit and loss (P&L) statement and is typically prepared quarterly or annually. For small businesses with few income streams, you might generate single-step income statements on a regular basis and a multi-step income statement annually.
Using an income statement to demonstrate a consistent history of income and profitability can make this process easier. The income statement serves as a tool to understand the profitability of your business. The income statement can also help you make decisions about your spending and overall management of business operations. Income statements should be generated quarterly and annually to provide visibility throughout the year.
Ultimately, horizontal analysis is used to identify trends over time—comparisons from Q1 to Q2, for example—instead of revealing how individual line items relate to others. As a working professional, business owner, entrepreneur, or investor, knowing how to read and analyze data from an income statement—one of the most important financial documents companies produce—is a critical skill to have. They use competitors’ P&L to gauge how well other companies are doing in their space and whether or not they should enter new markets and try to compete with other companies. Internal users like company management and the board of directors use this statement to analyze the business as a whole and make decisions on how it is run. For example, they use performance numbers to gauge whether they should open new branch, close a department, or increase production of a product.
